Navigating the Crypto and NFT Tax Maze: A Creator’s Guide
As an NFT creator, I’ve been navigating the ever-evolving crypto landscape, and I know firsthand how daunting the tax implications can be. While the crypto ecosystem continues to expand, with non-fungible tokens (NFTs) emerging as an exciting new frontier, understanding the nuances of crypto and NFT taxes is crucial for maintaining a successful and profitable creative journey.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll share my insights and strategies to empower you, fellow NFT creators, as you traverse the complex world of crypto and NFT taxes. From the basics of NFT taxation to practical tips for minimizing your tax liability, I’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools you need to thrive in this dynamic industry.
Understanding the NFT Tax Landscape
Let’s start by exploring the fundamental concepts of NFT taxation. NFTs, or non-fungible tokens, are unique digital assets that leverage blockchain technology to establish ownership and scarcity. Unlike traditional cryptocurrencies, each NFT is one-of-a-kind, making them a prime target for collectors and investors.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has classified NFTs as digital assets, similar to cryptocurrencies. This means that the same tax principles apply to your NFT transactions as they do to your crypto dealings. Whether you’re buying, selling, or creating NFTs, it’s essential to keep meticulous records and understand the potential tax implications.
One crucial consideration is the possibility of NFTs being classified as “collectibles” by the IRS. This special tax category carries a higher long-term capital gains rate of 28%, as opposed to the typical 15-20% rate for other capital assets. The IRS evaluates NFTs on a case-by-case basis to determine if they fall under the collectible designation, so it’s important to stay informed and proactive.
 The tax implication of NFTs
The tax implication of NFTs
Tax Implications for NFT Creators
As an NFT creator, you’ll navigate a unique set of tax considerations. Let’s dive into the specifics:
Minting NFTs
The act of minting an NFT, or creating a new digital asset on the blockchain, is not a taxable event in itself. However, when you sell your NFT, the transaction is considered a taxable event, and you’ll need to report the income as ordinary income.
It’s important to note that the gas fees associated with minting your NFT can be added to your cost basis, potentially reducing your tax liability when you eventually sell the NFT.
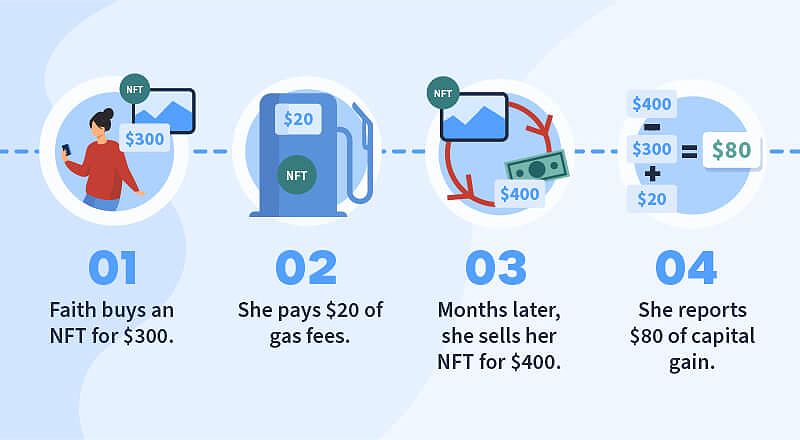 Gas fee tax for buying NFT
Gas fee tax for buying NFT
Selling NFTs
When you sell an NFT, the proceeds are generally taxed as ordinary income. This applies to both primary sales (the initial sale of an NFT) and secondary sales (subsequent sales on the secondary market). The tax rate will be determined by your personal income tax bracket, which can range from 10% to 37% at the federal level.
If the IRS deems your NFT a collectible, you may be subject to the higher 28% long-term capital gains rate on any gains from the sale, provided you held the NFT for more than one year.
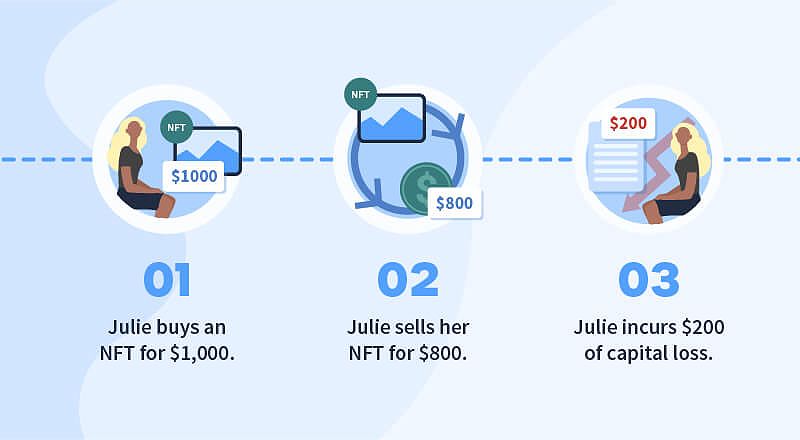 Selling NFT for fiat
Selling NFT for fiat
Royalty Income
Many NFT creators receive ongoing royalty payments when their NFTs are resold on the secondary market. These royalty payments are also considered ordinary income and subject to both federal income tax and self-employment tax (if your NFT activities constitute a business).
Self-Employment Tax
If your NFT creation and sales activities are considered a trade or business, you may be subject to self-employment tax in addition to your regular income tax. This self-employment tax rate is currently 15.3% and covers your Social Security and Medicare contributions.
To minimize your self-employment tax liability, be sure to track all eligible business expenses, such as software, marketing, and legal fees, as these can be deducted from your taxable income.
NFT Marketplaces and Reporting
When it comes to reporting your NFT transactions, keep in mind that not all NFT marketplaces provide tax forms or documentation. It’s your responsibility as the NFT creator to maintain detailed records of your sales, purchases, and other relevant transactions.
I recommend using tax software or a spreadsheet to keep track of your NFT activity, as this will make it easier to accurately report your income and deductions when filing your tax return.
 NFT Ethereum wallet taxes
NFT Ethereum wallet taxes
Strategies for Minimizing Crypto and NFT Taxes
While you can’t completely avoid paying taxes on your NFT-related income, there are several strategies you can employ to minimize your tax burden:
Long-Term Holding
If you hold your NFTs for more than one year, any gains from the sale may be eligible for the lower long-term capital gains tax rate, which ranges from 0% to 20% depending on your income level. This can be particularly beneficial if the IRS classifies your NFT as a collectible, as the long-term rate for collectibles is capped at 28%.
Tax-Loss Harvesting
If you’ve incurred losses from selling your NFTs, you can use these losses to offset capital gains from other investments, reducing your overall tax liability. This process, known as tax-loss harvesting, can be a powerful tool in managing your crypto and NFT tax obligations.
Tracking Business Expenses
As an NFT creator, I’ve found it crucial to keep meticulous records of all my business-related expenses, such as software subscriptions, marketing costs, and legal fees. These expenses can be deducted from your taxable income, potentially lowering your overall tax bill.
Consult a Tax Professional
Given the evolving nature of crypto and NFT taxation, I highly recommend consulting a tax professional who specializes in this area. They can help you navigate the complexities, ensure you’re in compliance with all relevant regulations, and develop a tailored tax strategy to minimize your liabilities.
 NFT Tax Software
NFT Tax Software
Additional Tax Considerations
While the primary focus has been on the tax implications for NFT creators, there are a few additional areas worth exploring:
Taxes for NFT Collectors and Investors
If you’re an NFT collector or investor, your tax obligations may differ slightly from those of creators. When you buy an NFT using cryptocurrency, the IRS treats it as a two-part transaction: first, the sale of your crypto, which is subject to capital gains tax, and then the purchase of the NFT. Similarly, when you sell an NFT, the gain or loss is subject to capital gains tax.
Taxes for NFT Airdrops and Staking
Receiving NFTs through airdrops or earning them through staking activities may also have tax consequences. The IRS generally considers airdrops as ordinary income, taxable at the fair market value of the NFTs at the time of receipt. Staking rewards may be subject to either ordinary income tax or capital gains tax, depending on the specific circumstances.
International NFT Tax Considerations
As the global adoption of NFTs continues to grow, it’s essential to understand the tax implications in various jurisdictions. While many countries follow similar principles to the IRS, there may be unique nuances or regulations that apply to your specific situation. If you’re engaging in cross-border NFT transactions, be sure to consult with a tax professional who specializes in international crypto and NFT taxation.
FAQ
Do I need to pay taxes on gas fees associated with minting NFTs?
Yes, gas fees related to minting your NFTs can be added to your cost basis, potentially reducing your tax liability when you eventually sell the NFT.
How do I report my NFT income on my tax return?
You’ll likely need to use Form 1040 (U.S. Individual Income Tax Return) along with Schedule C (Profit or Loss From Business) and Schedule SE (Self-Employment Tax) to report your NFT income.
What if I receive royalty payments in crypto?
You’ll need to report the value of your royalty income in crypto at the time you received it, and you may be subject to self-employment tax on that income.
Conclusion
As an NFT creator, navigating the complex world of crypto and NFT taxes can feel daunting, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can ensure your NFT-related activities remain profitable and compliant. By understanding the tax implications, tracking your transactions meticulously, and working with a tax professional, you can embrace the exciting opportunities presented by the NFT landscape while mitigating your tax liabilities.
In the ever-evolving crypto ecosystem, staying up-to-date with the latest tax guidance is crucial. Whether you’re a seasoned NFT creator or just beginning to explore the world of digital assets, taking the time to understand the tax implications can help you make informed decisions and maximize your profits. By navigating the crypto and NFT tax landscape with care and diligence, you can unlock the full potential of this rapidly growing industry and continue to push the boundaries of creativity.

















 Bitcoin
Bitcoin  Ethereum
Ethereum  Tether
Tether  XRP
XRP  Solana
Solana  USDC
USDC  Dogecoin
Dogecoin  Cardano
Cardano  TRON
TRON